

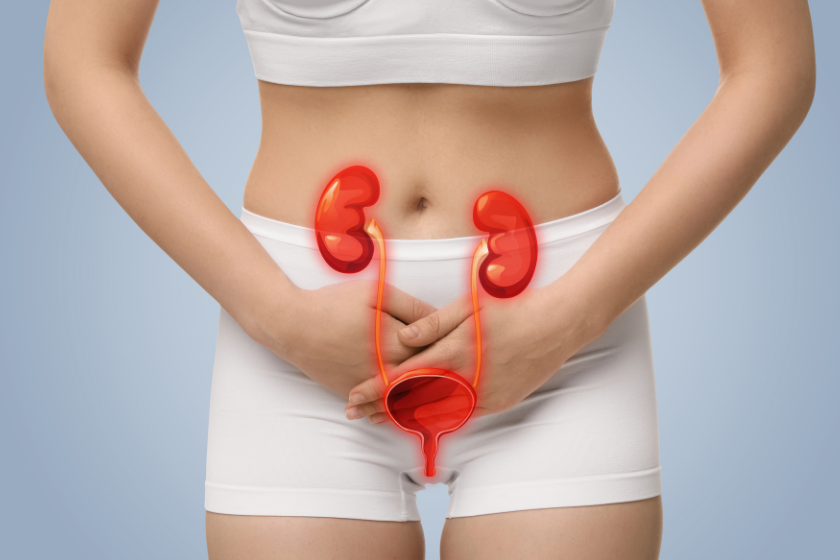
Urinary infections (UI) are infections that affect the urinary system, which includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. These infections are more common in women, although they can also affect men and children. Urinary infections can be asymptomatic or present various symptoms, and their treatment is essential to prevent complications.
Patients often ask about the typical symptoms of a urinary infection, which include pain or burning during urination, an urgent and frequent need to urinate, cloudy or foul-smelling urine, and in some cases, pain in the lower abdomen or back.
People often want to know what causes a urinary infection. The most common cause is the presence of bacteria, such as Escherichia coli (E. coli), that enter the urinary tract. Risk factors include poor hygiene, sexual intercourse, hormonal changes, and obstructions in the urinary tract.
Patients often ask how the diagnosis is made. Diagnosis is typically performed through a urinalysis to detect bacteria, white blood cells, or red blood cells. In some cases, a urine culture may be performed to identify the exact type of bacteria.
Many want to know what the appropriate treatment is. Urinary infections are typically treated with antibiotics prescribed by a doctor. It is important to complete the entire course of treatment, even if symptoms improve early. Additionally, drinking plenty of water and maintaining good hygiene is recommended.