

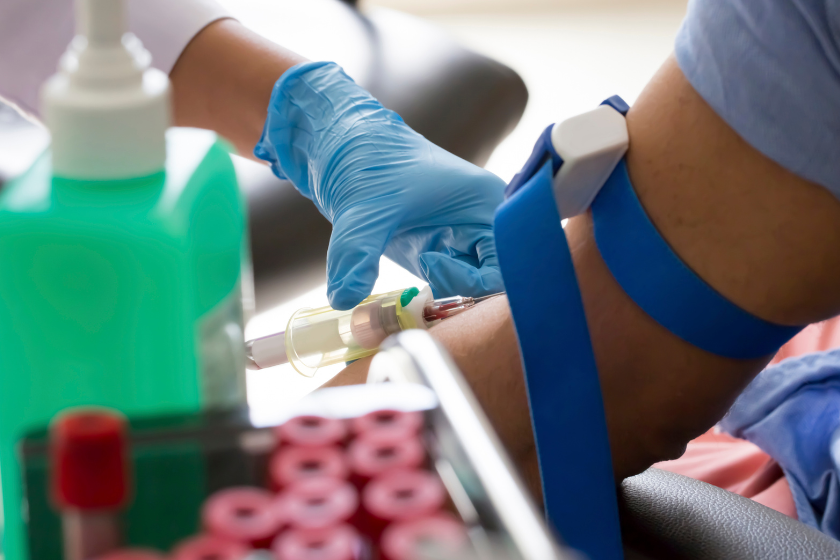
Blood tests are essential diagnostic tools used to assess a person's general health, detect diseases, and monitor health over time. These tests are conducted by taking a blood sample, which is then sent to a laboratory for analysis.
Measures components of the blood like red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets, providing information about overall health and the presence of anemia or infections.
Measures cholesterol and triglyceride levels to assess the risk of heart disease.
Analyze liver enzymes and other substances to assess liver health.
Measure blood sugar levels to detect diabetes or prediabetes.
Evaluate thyroid function by measuring specific hormones.
There are various types of blood tests, including the Complete Blood Count (which measures red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets), the Lipid Profile (which measures cholesterol and triglyceride levels), and Glucose Tests (which measure blood sugar levels). Each test provides important information about different aspects of health.
Preparation for a blood test can vary depending on the type of test. It is often recommended to fast for 8-12 hours before the test, especially for glucose and lipid profile tests. It is important to follow your doctor's or laboratory's instructions.
During a blood draw, a healthcare professional will clean the area with disinfectant, apply a tourniquet to make the veins more visible, and then insert a needle into the vein to draw the blood. The procedure is quick, and while some people may feel slight discomfort, it generally does not cause significant pain.
The time it takes to receive blood test results can vary depending on the type of test and the laboratory. Some tests may have results available the same day, while others may take several days. It is advisable to ask the lab or your doctor about the estimated time for results.